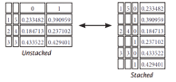
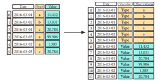
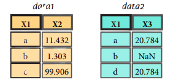
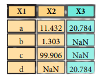
Pandas Cheat Sheet: Data Wrangling in Python
This cheat sheet is a quick reference for data wrangling with Pandas, complete with code samples.
Jun 2021 · 4 min read
RelatedSee MoreSee More
Exploring Matplotlib Inline: A Quick Tutorial
Learn how matplotlib inline can enable you to display your data visualizations directly in a notebook quickly and easily! In this article, we cover what matplotlib inline is, how to use it, and how to pair it with other libraries to create powerful visualizations.
Amberle McKee
How to Use the NumPy linspace() Function
Learn how to use the NumPy linspace() function in this quick and easy tutorial.
Adel Nehme
Python Absolute Value: A Quick Tutorial
Learn how to use Python's abs function to get a number's magnitude, ignoring its sign. This guide explains finding absolute values for both real and imaginary numbers, highlighting common errors.
Amberle McKee
How to Check if a File Exists in Python
Learn how to check if a file exists in Python in this simple tutorial
Adel Nehme
Writing Custom Context Managers in Python
Learn the advanced aspects of resource management in Python by mastering how to write custom context managers.
Bex Tuychiev
How to Convert a List to a String in Python
Learn how to convert a list to a string in Python in this quick tutorial.
Adel Nehme